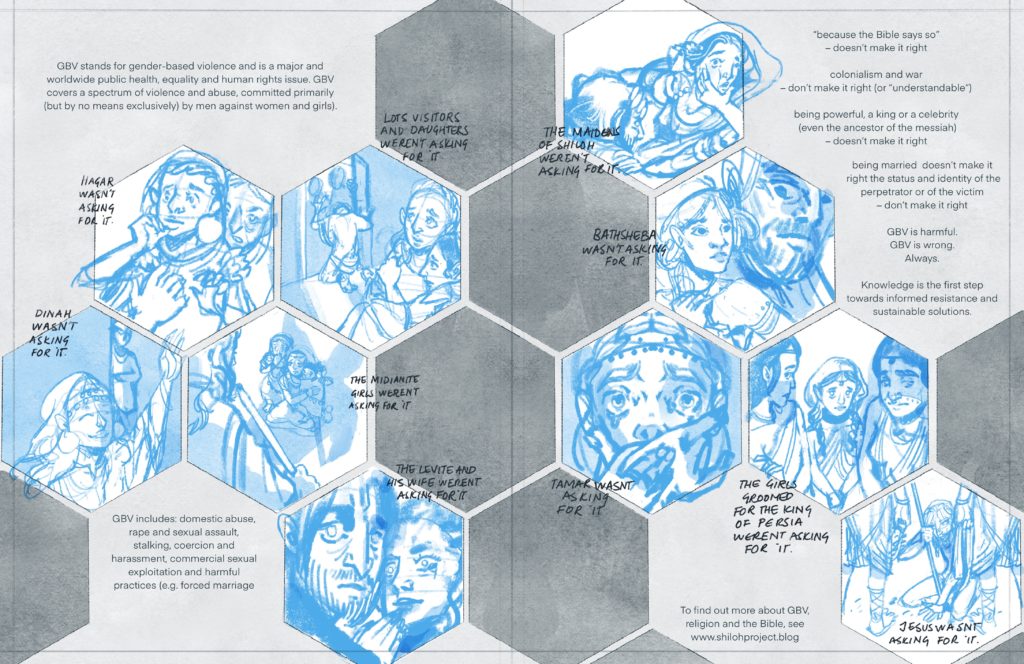
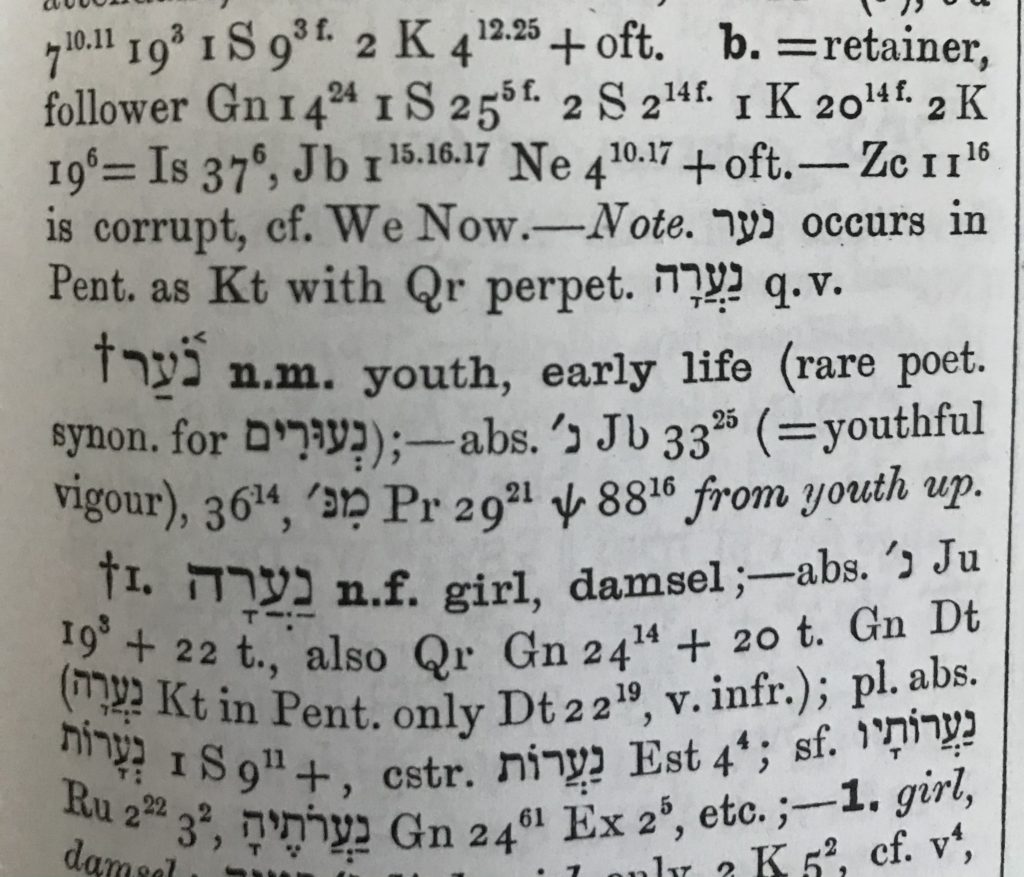Shiloh directors have been busy with their day jobs, but work goes on and there are some great posts in the pipeline…
If you haven’t already, please check out Noirthern – the magnificent blog and podcast on crime fiction in Scottish and Northern English settings. Given that the hosts are none other than Caroline Blyth and Katie Edwards, the (wide-ranging and wonderful) conversations often veer into the territories of rape culture and religion. But it’s far from relentlessly grim.
Shiloh followers might appreciate particularly Episode 4, ‘Saints and Saviour Syndrome’ (focused on Durham) and Episode 5, ‘Tartan Noir’ (focused on Glasgow and Liam McIlvanney’s The Quaker, which draws inspiration from the notorious and unsolved Bible John case).
We hope to have some exciting updates soon… including about restarting suspended research project activities and a call for papers for a fabulous publication.
Watch this space!
[The feature image is adapted from artwork by Melody Clark. Please see: https://www.etsy.com/people/mellyemclark? ]
Noirthern is funded in part by a grant from AHRC/UKRI.